
1031 Exchange
What is a 1031 Exchange In Hawaii?
A 1031 Exchange in Hawaii is a real estate investing tool that allows you to exchange your Hawaii investment property for another of the same type and defer capital gains taxes that you would otherwise have to pay at the time of sale.
- Named in reference to 26 U.S. Code § 1031, the U.S. Internal Revenue Code
- “Like-kind” properties are properties of the same nature or character even if they differ in quality. For example, an apartment building is generally considered “like-kind” to another apartment building.
- What is an investment property? Property held for productive use in a trade or business or for investment.
Why Should You Consider a 1031 Exchange?
The largest benefit of utilizing a 1031 Exchange is the deferral of capital gains tax, which allows you to use more capital for the replacement property.
Other reasons to consider a 1031 Exchange include:
- Relocating an asset and equity
- Increasing cash flow
- With proper estate planning, accrued deferred capital gains tax can be completely eliminated when real estate is passed on to heirs
Three Main Rules for a 1031 Exchange

Your Hawaii real estate must be used for investment or business purposes. Not a primary residence.

Replacement property must be identified within 45 days and purchased within 180 days.

If the value of the replacement property is less than the relinquished property, the difference is called a boot and it is taxable.
Types of 1031 Exchanges available
- Forward- Sell relinquished property then buy replacement property
- Reverse- Buy Replacement property then sell relinquished property
- Partial- Partially tax deferred transaction rather than deferring all their taxes
- . The portion of the exchange proceeds not reinvested is called “boot” and is subject to capital gains and depreciation recapture taxes.

Capital Gains Tax and the 1031 Exchange
As you’re aware, capital gains tax is the amount of tax owed on the profit you make on an investment or asset when you sell it, and this number is calculated by subtracting the asset’s original cost plus any expenses incurred, such as improvements, depreciation, etc. from the final sale price.
Net Selling Price (Selling Price – Cost of Selling)
–
Adjusted Cost Basis (Cost Basis + Improvements – Depreciation)
=
Capital Gains
Carry Over Cost Basis vs. Step Up In Cost Basis
A carry over basis is a method for determining the tax basis of an asset when it is transferred from one individual to another. A carry over basis is often used when one party leaves assets or property to another person as a gift. In this situation, the basis often remains the same as when the giver held the asset.
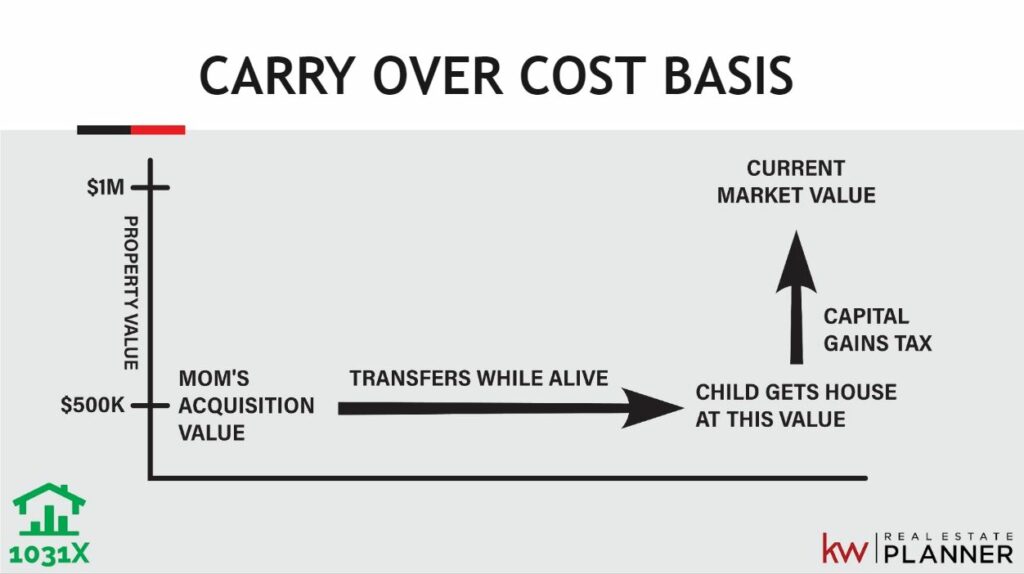
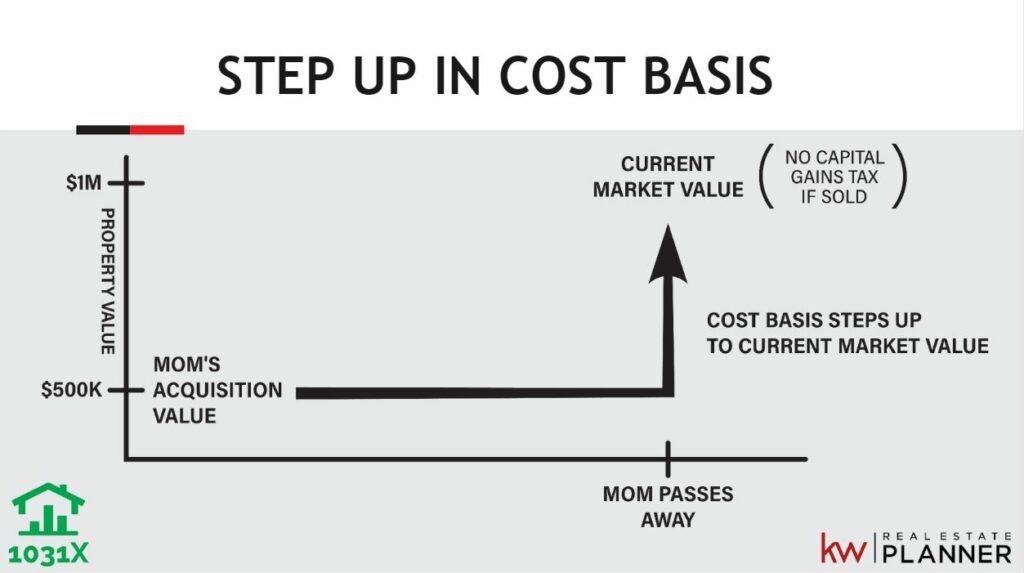
Step-up in cost basis refers to the adjustment in the cost basis of an inherited asset to its fair market value on the date of the decedent’s death.
This occurs when the price of an inherited asset on the date of the decedent’s death is above its original purchase price. The tax code allows for the raising of the cost basis to the higher price, minimizing the capital gains taxes owed if the asset is sold later.
Delaware Statutory Trust
Another 1031 Exchange option to be aware of is the Delaware Statutory Trust (DST), which offers investors the opportunity to exchange into properties that might otherwise be beyond reach. DSTs allow 500 accredited investors to pool their funds in order to purchase ownership interests in properties like retail centers, office buildings, and apartment complexes.
Some benefits to DSTs include, but aren’t limited to, no management responsibilities, portfolio diversification, and limited personal liability.
Overall Benefits
- Defer long term capital gains taxes
- State Capital Gains Tax varies by state
- Fed up to 20% + AGI > $400k add 3.8%
- Apply all proceeds to replacement property to increase buying power
- Exchange can involve multiple properties to provide greater diversity or consolidation to upgrade investments
- Great tool for estate planning
- Allow adult children to pre-determine their inheritance if planned in advance
- Long Term Capital Gains applies to properties held for more than 12 months.
- Short Term Capital Gains tax is taxed as ordinary income
1031 Exchange programs in Hawaii can be confusing. Before deciding if a 1031 Exchange is right for your property, reach out to our team by clicking the contact link below. If you would like a free analysis of the value of your home, we are more than happy to assist you!


